What is Skin Whitening Treatment
Skin whitening treatment, also known as skin lightening or skin bleaching, encompasses a variety of cosmetic procedures aimed at reducing the melanin content in the skin. Melanin is the pigment responsible for skin color, and skin whitening treatments aim to lighten the skin tone by decreasing the production or concentration of melanin. These treatments are often sought after to address issues such as hyperpigmentation, uneven skin tone, dark spots, and overall skin discoloration. It’s important to understand that skin whitening treatments can range from over-the-counter products to professional procedures performed by dermatologists or qualified medical professionals. The effectiveness and safety of these treatments vary widely, and it’s crucial to research and understand the potential risks and benefits before undergoing any procedure.
Different Types of Skin Whitening Treatments
A wide array of treatments are available for skin whitening, each with its own mechanism of action, benefits, and potential side effects. These treatments can be broadly categorized into topical creams, chemical peels, laser therapy, oral medications, and physical exfoliation methods such as microdermabrasion. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the individual’s skin type, the severity of the pigmentation issues, and personal preferences. It’s imperative to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and ensure the safety and efficacy of the chosen procedure.
Topical Creams

Topical creams are among the most common and accessible skin whitening treatments. These creams typically contain ingredients such as hydroquinone, retinoids, corticosteroids, kojic acid, and arbutin, which work by inhibiting melanin production or promoting skin cell turnover. Hydroquinone is a potent skin-lightening agent, but it can cause side effects such as skin irritation and ochronosis (a permanent darkening of the skin). Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, help to exfoliate the skin and promote cell turnover, leading to a brighter complexion. Other ingredients like kojic acid and arbutin are known for their skin-lightening properties and are often used in combination with other agents to enhance effectiveness. The use of topical creams should always be under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate the outer layers and promote the growth of new, evenly pigmented skin. The strength and type of chemical peel determine the depth of exfoliation and the resulting skin-lightening effect. Superficial peels, using alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid or lactic acid, are mild and address surface-level pigmentation issues. Medium-depth peels, containing trichloroacetic acid (TCA), penetrate deeper into the skin and can treat more significant discoloration. Deep peels, using phenol, are the strongest and can produce dramatic results but also carry the highest risk of side effects. Chemical peels should always be performed by a qualified professional to minimize the risk of complications such as scarring, infection, and changes in skin pigmentation.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy utilizes focused light beams to target and break down melanin in the skin. Different types of lasers can be used, including Q-switched lasers and fractional lasers, depending on the specific skin condition and desired outcome. Laser treatments can effectively reduce the appearance of dark spots, sun damage, and uneven skin tone. The laser energy is absorbed by the melanin, which breaks it down and allows the body to eliminate it naturally. Laser therapy is a more targeted approach compared to some other treatments, but it can also carry risks such as hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation, and scarring. Proper aftercare and sun protection are crucial to prevent complications and maintain the results of laser treatments. Always consult with a qualified dermatologist for laser skin whitening treatments.
Oral Medications
In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to reduce melanin production and lighten the skin. These medications often contain ingredients like glutathione or tranexamic acid, which can inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase, responsible for melanin synthesis. Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that can also help detoxify the body, and some studies suggest it may have skin-lightening effects. Tranexamic acid is typically used to treat melasma and can help reduce pigmentation by interfering with the inflammatory processes. Oral medications can have systemic effects and may cause side effects, so it’s crucial to discuss the risks and benefits with a dermatologist and monitor any potential adverse reactions.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a device to exfoliate the skin’s outer layer, removing dead skin cells and stimulating new cell growth. This can help to improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of dark spots, and promote a more even skin tone. Microdermabrasion typically involves the use of a handheld device that sprays tiny crystals onto the skin, which are then vacuumed away, along with the exfoliated skin cells. While microdermabrasion is generally a safe procedure, it may cause temporary redness, swelling, and sensitivity. Multiple sessions are usually required to achieve noticeable results, and the effectiveness of microdermabrasion can vary depending on the individual’s skin type and the severity of the pigmentation issues. Microdermabrasion may be used as a supplementary treatment.
7 Important Facts About Skin Whitening Treatment
Fact 1 Understand the Risks

Before embarking on any skin whitening treatment, it is crucial to fully understand the potential risks involved. These can include skin irritation, inflammation, allergic reactions, and changes in skin pigmentation, such as hyperpigmentation (darkening) or hypopigmentation (lightening). Certain treatments, like those containing hydroquinone, can cause ochronosis, a permanent skin discoloration. Always research the potential side effects and discuss them with a dermatologist before proceeding with any treatment.
Fact 2 Research Your Options
Thorough research is essential when considering skin whitening treatments. Educate yourself about the different types of treatments available, their mechanisms of action, and their potential benefits and risks. Look for reliable sources of information, such as reputable medical journals, dermatological websites, and consultations with qualified professionals. Avoid relying solely on anecdotal evidence or unsubstantiated claims, and always prioritize treatments that are supported by scientific evidence and performed by trained professionals.
Fact 3 Consult a Dermatologist
The most important step in the skin whitening treatment journey is consulting with a board-certified dermatologist. A dermatologist can assess your skin type, evaluate your specific pigmentation concerns, and recommend the most appropriate and safe treatment options. They can also explain the potential risks and benefits of each treatment, monitor your progress, and address any side effects that may arise. Never attempt any skin whitening treatment without first consulting with a qualified dermatologist.
Fact 4 Be Patient and Realistic
Skin whitening treatments typically require patience and realistic expectations. Results are not always immediate, and it may take several weeks or months to see noticeable improvements. Furthermore, achieving the desired skin tone may not always be possible, and the effectiveness of treatment can vary depending on individual factors. Be realistic about the potential outcomes and understand that maintaining the results often requires ongoing maintenance and sun protection.
Fact 5 Consider Maintenance
Skin whitening treatments often require ongoing maintenance to sustain the results. This may include regular use of topical creams, chemical peels, or laser treatments. It also involves adopting a consistent skincare routine that includes sun protection, as sun exposure can counteract the effects of the treatment and lead to further pigmentation. Following your dermatologist’s recommendations for maintenance is crucial to preserving your results and maintaining healthy skin.
Fact 6 Watch for Side Effects
It is important to be vigilant and watch for any side effects during and after skin whitening treatments. Common side effects include skin irritation, redness, itching, and dryness. More serious side effects, such as allergic reactions, blistering, changes in pigmentation, or scarring, can also occur. If you experience any adverse reactions, discontinue the treatment immediately and consult your dermatologist. Prompt attention to side effects can help minimize complications and ensure the best possible outcome.
Fact 7 Protect Your Skin from the Sun
Sun protection is paramount for anyone undergoing skin whitening treatments. Exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can worsen pigmentation issues, counteract the effects of treatment, and increase the risk of skin damage. Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and reapply it every two hours, especially when outdoors. Wear protective clothing, such as hats and long sleeves, and seek shade during peak sun hours. Consistent sun protection is essential for maintaining the results of skin whitening treatments and preventing future pigmentation concerns.
Benefits of Skin Whitening Treatment
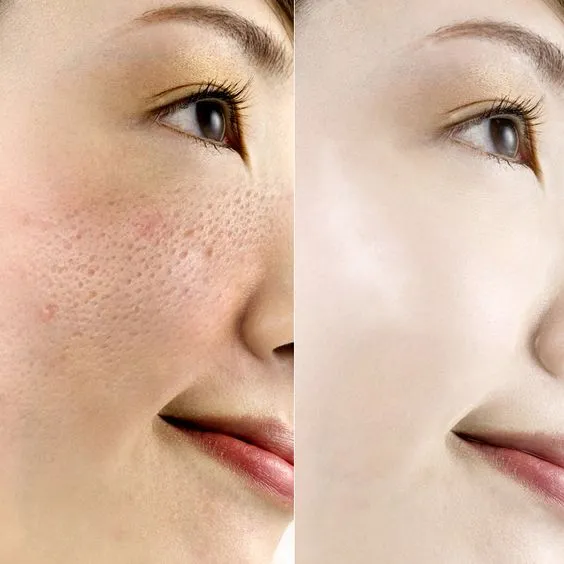
Skin whitening treatments can offer a range of benefits for individuals seeking to improve their skin appearance. These benefits include the reduction of hyperpigmentation, such as dark spots, sunspots, and age spots, leading to a more even skin tone. They can also help to lighten areas of discoloration caused by acne scars, melasma, or other skin conditions. Additionally, skin whitening treatments can enhance overall skin radiance and improve the texture, leading to a more youthful and revitalized appearance. It is important to have realistic expectations and to prioritize skin health throughout the process.
Risks and Side Effects of Skin Whitening Treatment
While skin whitening treatments can offer cosmetic benefits, it is crucial to be aware of the potential risks and side effects. These can include skin irritation, redness, and dryness, particularly with the use of topical creams containing harsh ingredients. More serious side effects may include allergic reactions, blistering, and changes in skin pigmentation, such as hyperpigmentation (darkening) or hypopigmentation (lightening). Certain treatments, like those containing hydroquinone, can lead to ochronosis, a permanent skin discoloration. It is important to consult with a dermatologist to discuss the potential risks and side effects associated with any specific treatment.
Conclusion
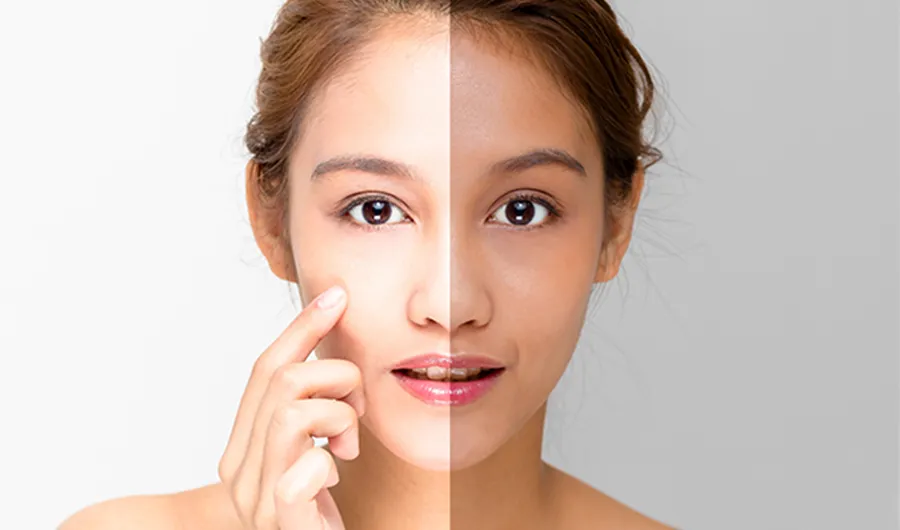

Skin whitening treatments offer a range of options for those seeking to address pigmentation concerns and improve their skin tone. However, it is essential to approach these treatments with caution, thorough research, and the guidance of a qualified dermatologist. Understanding the various types of treatments, their potential benefits, risks, and the importance of sun protection and maintenance is crucial for making informed decisions. By following these guidelines, individuals can strive for safer and more effective results in their skin-whitening journey. Prioritizing skin health and seeking professional advice are key to achieving a healthy and radiant complexion.
